Tutorial - Understanding Recursion
Tutorial
Compiled from multiple sources on the internet.
Since this is a tutorial, there is no submission data for this. Please use the IDE for practice.
RECURSION
A function that calls itself is known as a recursive function. And, this technique is known as recursion.
How recursion works..
Syntax
void recurse()
{
... .. ...
recurse();
... .. ...
}
int main()
{
... .. ...
recurse();
... .. ...
}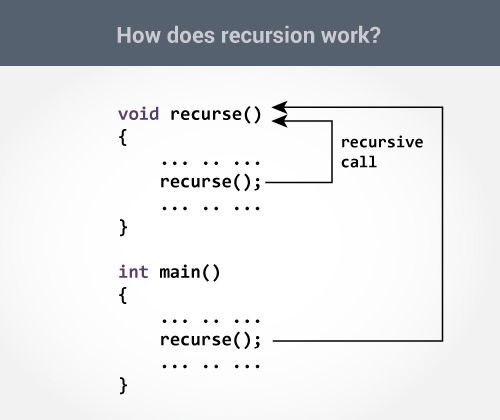
The recursion continues until some condition is met to prevent it.
To prevent infinite recursion, if...else statement (or similar approach) can be used where one branch makes the recursive call, and other doesn't.
Example: Sum of Natural Numbers Using Recursion
#include <stdio.h>
int sum(int n);
int main() {
int number, result;
printf("Enter a positive integer: ");
scanf("%d", &number);
result = sum(number);
printf("sum = %d", result);
return 0;
}
int sum(int n) {
if (n != 0)
// sum() function calls itself
return n + sum(n-1);
else
return n;
}Output:
Enter a positive integer:3
sum = 6Initially, the sum() is called from the main() function with number passed as an argument.
Suppose, the value of n inside sum() is 3 initially. During the next function call, 2 is passed to the sum() function. This process continues until n is equal to 0.
When n is equal to 0, the if condition fails and the else part is executed returning the sum of integers ultimately to the main() function.

Advantages and Disadvantages of Recursion
Recursion makes program elegant. However, if performance is vital, use loops instead as recursion is usually much slower.
Exercise:
The following example calculates the factorial of a given number using a recursive function. Fill in the blank with the correct recursive call to get the result: Note: Factorial of 12 is 479001600 −
#include <stdio.h>
unsigned long long int factorial(unsigned int i) {
if(i <= 1) {
return 1;
}
return i * _____________;
}
int main() {
int i = 12;
printf("Factorial of %d is %d\n", i, factorial(i));
return 0;
}Try out all the examples given in class now using the IDE.
Practice Exercises. Write programs in C :
- To find power of any number using recursion.
- To print all natural numbers between 1 to n using recursion
- To print all even or odd numbers in given range using recursion.
- To find sum of all natural numbers between 1 to n using recursion.
- To find sum of all even or odd numbers in given range using recursion.
- To find reverse of any number using recursion.
- To check whether a number is palindrome or not using recursion.
- To find sum of digits of a given number using recursion.
- To find factorial of any number using recursion.
- To generate nth Fibonacci term using recursion.
- To find GCD (HCF) of two numbers using recursion.
- To find LCM of two numbers using recursion.
- To display all array elements using recursion.
- To find sum of elements of array using recursion.
- To find maximum and minimum elements in array using recursion.
Comments
.
include <stdio.h> int main() { printf("HeLLo WoRLD"); }
include <stdio.h>
int main() { printf("HeLLo WoRLD"); }